BT.601 / Rec.601
also known as Rec. 601 and former name CCIR 601
Description
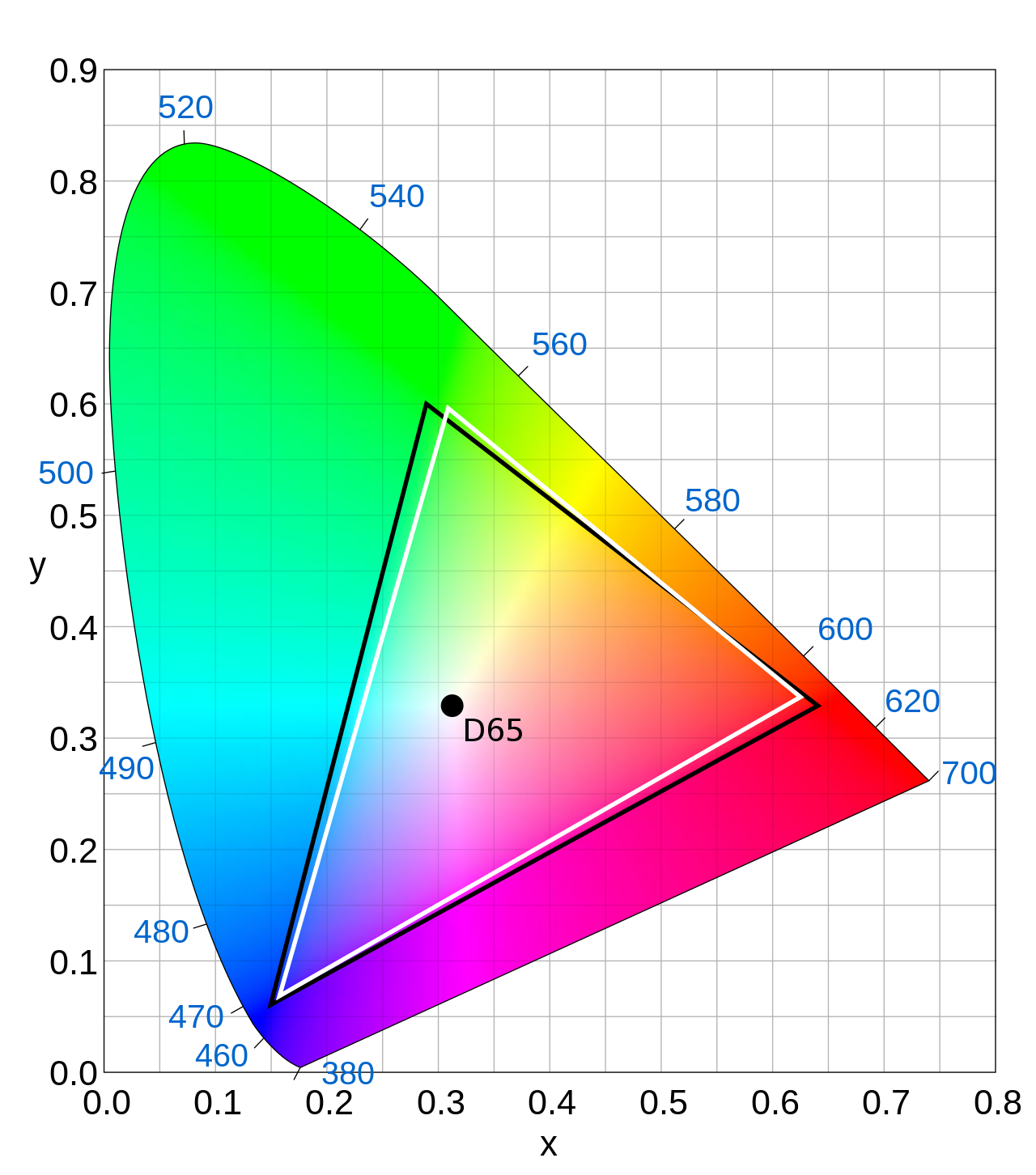
Diagram of the CIE 1931 color space that shows the Rec. 601 (SDTV) color space in the triangle. Black corresponds to 625 line (PAL and SECAM) systems, white to 525 lines (NTSC SMPTE C primaries). Rec. 601 uses Illuminant D65 for the white point.
ITU-R Recommendation BT.601, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 601 or BT.601 (or its former name CCIR 601) is a standard originally issued in 1982 by the CCIR (an organization, which has since been renamed as the International Telecommunication Union – Radiocommunication sector) for encoding interlaced analog video signals in digital video form. It includes methods of encoding 525-line 60 Hz and 625-line 50 Hz signals, both with an active region covering 720 luminance samples and 360 chrominance samples per line. The color encoding system is known as YCbCr 4:2:2.
The Rec. 601 video raster format has been re-used in a number of later standards, including the ISO/IEC MPEG and ITU-T H.26x compressed formats, although compressed formats for consumer applications usually use chroma subsampling reduced from the 4:2:2 sampling specified in Rec. 601 to 4:2:0.
The standard has been revised several times in its history. Its seventh edition, referred to as BT.601-7, was approved in March 2011 and was formally published in October 2011.
The Rec. 601 signal can be regarded as if it is a digitally encoded analog component video signal, and thus the sampling includes data for the horizontal and vertical sync and blanking intervals. Regardless of the frame rate, the luminance sampling frequency is 13.5 MHz. The samples are uniformly quantized using 8- or 10-bit PCM codes in the YCbCr domain.
Slightly different primaries are specified for the 625-line (PAL and SECAM) and 525-line (NTSC SMPTE C primaries) systems. Earlier versions of the standard (prior to BT.601-6, approved in January 2007) did not contain an explicit definition of the color primaries.